Common reasons for visa rejection: Understanding Visa Rejection Updated [2025/2026]

Embarking on the visa application journey can be one of the most anxiety-inducing aspects of international travel or relocation plans. Whether you’re applying for a tourist visa to explore new destinations, a student visa to pursue academic dreams, or a work visa to advance your career abroad, the possibility of rejection looms as a constant concern for many applicants.
Visa rejection is not just a possibility—it’s a reality that thousands of applicants face every day across the globe. Understanding why visas get rejected is crucial not only for those preparing to apply but also for those who have faced a disappointing denial and are seeking to understand what went wrong.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the most common reasons for visa rejection, providing you with the knowledge you need to either prepare a stronger application or make sense of a refusal you’ve already received. While specific requirements and scrutiny levels may vary between countries—whether you’re applying for a US visa, Schengen visa, UK visa, or others—the fundamental principles that lead to visa denials remain surprisingly consistent worldwide.
By identifying potential pitfalls before you apply, you can significantly increase your chances of approval and potentially save yourself time, money, and emotional distress.
Major Categories of Visa Rejection Reasons (Overview)
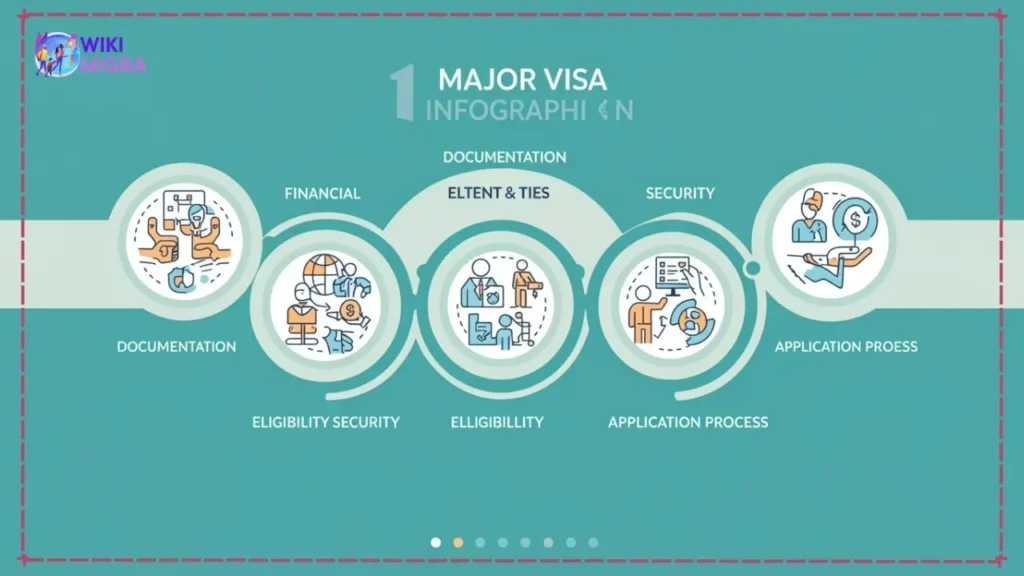
Before diving into specifics, it’s helpful to understand that most visa rejections fall into several key categories:
- Documentation Issues: Incomplete applications, missing documents, or errors in submitted materials
- Financial Concerns: Insufficient proof of funds or unclear sources of financial support
- Intent and Ties to Home Country: Failure to demonstrate that you’ll return home after your authorized stay
- Eligibility and Security Matters: Background issues, health concerns, or applying for the wrong visa type
- Application Process Problems: Poor interview performance or failure to follow specific instructions
Understanding these broad categories can help you focus your preparation efforts on the areas most likely to impact your application’s success. Now, let’s examine each of these in greater detail.
Documentation & Application Errors

Incomplete or Incorrect Application Forms
One of the most preventable yet frustratingly common reasons for visa denial is submitting forms with errors or missing information. When processing thousands of applications, immigration officials have little patience for forms that are:
- Missing required signatures
- Containing blank fields that should be completed
- Filled with inconsistent information (e.g., different spellings of your name)
- Using the wrong form entirely for your visa category
Case Example: Maria applied for a tourist visa but left the “accommodations” section blank because she planned to decide on hotels later. Her application was promptly rejected with instructions to provide complete accommodation details.
Visa applications require meticulous attention to detail. Even small oversights can lead to rejection, as they may raise questions about your attention to detail or, worse, your honesty.
Insufficient or Missing Supporting Documents
Different visa types require different supporting documentation, but nearly all applications demand substantial evidence to back up your claims and intentions. Common document-related rejections occur when applicants fail to provide:
- Required photographs meeting specific dimensional and background requirements
- Proof of relationship for dependent visas
- Letters of invitation or sponsorship
- Evidence of accommodation arrangements
- Travel itineraries or flight reservations
- Employment verification or business documentation
- Academic credentials for student visas
The key is to thoroughly research document requirements for your specific visa category and destination country. Many immigration websites provide detailed checklists—use these as your guide and double-check everything before submission.
Invalid or Expired Passport
Your passport is the foundation of your visa application, and issues with this critical document can immediately disqualify you. Visa officers routinely reject applications due to:
- Passports with less than six months validity beyond your planned stay
- Insufficient blank pages for visa stamps
- Damaged or mutilated passports
- Non-machine-readable or old-format passports
| Passport Requirement | Common Standard | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Validity Period | 6+ months beyond stay | Ensures document won’t expire during travel |
| Blank Pages | 2-4 pages minimum | Needed for entry/exit stamps and visa |
| Physical Condition | Undamaged, all pages intact | Damaged passports raise security concerns |
Before applying, check your passport’s expiration date and condition. If it’s close to expiration or damaged, consider renewing it before starting the visa application process.
Fraudulent Documents or Misrepresentation
Perhaps the most serious documentation issue—and one with lasting consequences—is submitting fraudulent materials or providing false information. This includes:
- Altered or counterfeit documents
- False statements on application forms
- Manipulated financial records
- Fake employment letters or academic credentials
- Concealing relevant information (such as previous visa denials or criminal history)
The consequences for document fraud or misrepresentation go far beyond a simple rejection. Many countries impose multi-year or even lifetime bans on applicants caught submitting fraudulent materials. Immigration systems increasingly share information, meaning a fraudulent application to one country could affect your ability to travel to others.
Always prioritize honesty over presenting an “ideal” application. If you have concerns about aspects of your situation, consult with an immigration attorney rather than resorting to misrepresentation.
Financial Insufficiency

Lack of Sufficient Funds
Immigration authorities need assurance that you can financially support yourself during your stay without working illegally or becoming dependent on public resources. Visa applications are frequently rejected when applicants fail to demonstrate:
- Enough money to cover all travel expenses
- Accommodation and daily living costs
- Emergency funds
- Return transportation costs
Different countries have different financial requirements. For example:
- Schengen countries typically require proof of approximately €50-100 per day of stay
- The UK visitor visa suggests showing about £95 per day for London stays
- US tourist visas have no fixed amount but expect “sufficient funds” relative to your travel plans
To avoid rejection on financial grounds:
- Research the specific financial requirements for your destination
- Provide bank statements covering several months (not just a recent deposit)
- Include evidence of regular income where applicable
- For sponsored trips, ensure proper sponsorship documentation
Unclear Source of Funds
Having money in your account isn’t always enough—visa officers also scrutinize where the money came from. Applications raise red flags when they show:
- Large, unexplained deposits shortly before application
- Account balances inconsistent with stated employment or income
- Funds that appear to be “parked” temporarily in accounts
- Multiple transfers between accounts that suggest attempts to inflate balances
To address this concern:
- Provide bank statements covering 3-6 months showing consistent financial history
- Include salary slips or income tax returns that align with your bank balances
- Explain any large deposits with supporting documentation
- For sponsored travel, clearly document the relationship with your sponsor and their ability to support you
Potential to Become a Public Charge
Some countries, particularly the United States, explicitly evaluate whether an applicant might become dependent on public assistance. This “public charge” ground for inadmissibility considers your:
- Age and health status
- Family situation and responsibilities
- Assets, resources, and financial status
- Education and skills
Those deemed likely to require government assistance may face rejection. This concern is especially relevant for immigrant visas or long-term stays but can affect temporary visa applications as well.
Tip: For countries with public charge concerns, consider providing evidence of health insurance coverage, employment prospects, or family support systems to address potential concerns.
You may be interested in: Canada Visa Processing Times | Your Ultimate 2025 Guide [Updated Monthly]
Issues with Intent & Ties (Especially for Non-Immigrant Visas)
Failure to Demonstrate Strong Ties to Home Country
For temporary visas (tourist, business, student), immigration officers must be convinced that you intend to return to your home country after your authorized stay. This is often the single most common reason for visa rejection, particularly for applicants from countries with high immigration rates or economic challenges.
Signs of strong ties to your home country include:
- Stable, ongoing employment
- Property ownership or long-term leases
- Family responsibilities (especially dependent children)
- Financial assets or investments
- Social and community connections
- Future obligations (upcoming work projects, enrolled educational programs)
When these ties appear weak or unconvincing, visa officers may presume you intend to remain in the destination country beyond your authorized stay.
For US visa applicants: This concern is formally codified under Immigration and Nationality Act Section 214(b), which presumes immigrant intent unless the applicant proves otherwise. Many US visa denials cite this specific provision.
Unclear or Unconvincing Purpose of Visit
Visa officers expect applicants to have a clear, legitimate reason for travel that aligns with the visa category requested. Applications are frequently rejected when the purpose appears:
- Vague or poorly defined
- Inconsistent with the applicant’s background
- Implausible given the timing or circumstances
- At odds with supporting documentation
For example, a tourist visa application claiming the purpose is “business meetings” raises category alignment questions, while an applicant with limited financial resources proposing an extended luxury vacation might face skepticism about their true intentions.
How to address this issue:
- Provide a detailed itinerary
- Include supporting documentation (hotel bookings, tour reservations, conference registrations)
- Ensure your stated purpose aligns logically with your personal and professional background
- Be prepared to discuss your plans articulately during interviews
Past Immigration Violations
Previous immigration infractions significantly increase the likelihood of visa rejection. Officers carefully review records for:
- Visa overstays (even short ones)
- Previous deportations or removals
- Violations of visa conditions (such as working on a tourist visa)
- Attempts to enter without proper authorization
- Prior visa denials (especially if for misrepresentation)
Many countries’ immigration systems share data, meaning violations in one country can affect applications to others. Some infractions trigger automatic bans for specific periods:
- Overstays of 180+ days may trigger multi-year bans in countries like the US
- Prior deportations often result in 5-10 year prohibitions on return
- Fraud or misrepresentation can lead to permanent ineligibility
If you have immigration violations in your history, consult with an immigration attorney before applying. In some cases, waivers may be available, but applying without addressing past issues usually results in rejection.
Eligibility, Security & Background Concerns
Criminal Record
Criminal history can render applicants inadmissible to many countries, though policies vary regarding which offenses are disqualifying. Common approaches include:
- “Moral turpitude” offenses (fraud, theft, violent crimes) typically trigger inadmissibility
- Drug-related convictions are particularly problematic for many countries
- Even minor offenses can be grounds for denial if recent
- Some countries distinguish between spent and unspent convictions
Many countries have waiver processes for certain offenses, particularly those that:
- Occurred in the distant past
- Were minor in nature
- Have been formally pardoned or expunged
If you have a criminal record, research the specific admissibility rules for your destination country and consider consulting with an immigration attorney before applying.
Health-Related Grounds
Health concerns can lead to visa rejection, particularly for long-term or immigrant visas. Common health-related grounds include:
- Communicable diseases of public health significance (varies by country but may include tuberculosis, HIV in some nations, and other infectious conditions)
- Failure to provide required vaccination records
- Physical or mental disorders associated with harmful behavior
- Drug addiction or abuse
Most countries require medical examinations for immigrant visas, and some require them for certain non-immigrant categories as well. These examinations must typically be performed by authorized physicians.
Security Risks
National security concerns are taken extremely seriously by all countries’ immigration systems. Applications may be rejected due to:
- Suspected ties to terrorist organizations
- Involvement in espionage or sabotage
- Participation in persecution or human rights abuses
- Membership in prohibited organizations
- Activities threatening public safety or national interests
Security checks are typically conducted behind the scenes, often involving database checks across multiple agencies and countries. If rejected on security grounds, limited information about specific concerns may be provided to the applicant.
Applying for the Wrong Visa Category
Each visa category has specific requirements and permitted activities. Applying for the wrong type of visa for your intended activities often leads to rejection. Common mismatches include:
- Planning to work while on a tourist visa
- Intending to study on a business visa
- Using a student visa primarily for employment
- Applying for a visitor visa when immigrant intent is evident
| Intended Activity | Appropriate Visa Type | Inappropriate Visa Type |
|---|---|---|
| Tourism/Visiting Family | Visitor/Tourist Visa | Business or Student Visa |
| Paid Work | Work Visa/Permit | Tourist, Business, or Student Visa |
| Academic Study | Student Visa | Tourist or Business Visa |
| Business Meetings | Business Visa | Tourist Visa (in some countries) |
Research the visa categories available for your destination country and select the one that specifically allows your planned activities.
Application Process Issues
Poor Interview Performance (If Applicable)
Many visa types require in-person interviews, and poor performance during these conversations frequently leads to denial. Common interview issues include:
- Providing inconsistent information compared to your written application
- Appearing unprepared or unknowledgeable about your travel plans
- Giving vague or evasive answers to direct questions
- Showing nervousness that might be interpreted as deception
- Demonstrating poor communication skills or language barriers
To perform well in visa interviews:
- Review your application thoroughly before the interview
- Practice explaining your travel plans concisely
- Prepare for likely questions about your ties to home and travel purpose
- Bring organized supporting documentation
- Dress professionally and arrive early
Remember that visa officers conduct many interviews daily and develop intuition about applicants. Honesty and straightforwardness are more effective than memorized answers.
Failure to Follow Instructions
Immigration processes have specific, often rigid procedural requirements. Applications may be rejected when applicants:
- Miss appointment deadlines
- Ignore specific submission guidelines
- Fail to respond to requests for additional information
- Don’t follow biometric collection procedures
- Submit materials in incorrect formats
These procedural failures may seem minor, but they can signal to immigration authorities that an applicant might not follow immigration rules after entry.
What Happens After a Rejection?
Receiving a visa rejection can be frustrating and disappointing, but it doesn’t necessarily mean the end of your travel plans. Understanding your options requires first understanding the specific reason for denial.
1. Review Your Refusal Letter Carefully
Most countries provide some form of explanation for visa denials, though the level of detail varies greatly:
- US rejections often cite specific legal provisions (like 214(b)) without extensive detail
- Schengen visa rejections typically include checkboxes indicating specific grounds for refusal
- UK and Canadian refusals generally provide more detailed explanations
This information is crucial for determining your next steps.
2. Consider Your Options
Depending on the country and visa type, you may have several options:
- Reapplication – Most common approach, especially when addressing deficiencies in documentation or financial evidence
- Appeal – Available for some visa types in certain countries, though often limited to procedural errors rather than merits
- Administrative/Judicial Review – Legal challenges to visa decisions, available in limited circumstances
- Waiver Requests – For certain grounds of inadmissibility, waivers may be available
3. Improve Your Application
If reapplying, focus on strengthening the specific areas mentioned in your refusal:
- Provide additional documentation addressing the concerns
- Improve demonstration of ties to your home country
- Clarify the purpose and itinerary of your trip
- Consider timing (sometimes applying during a different season helps)
How to Minimize the Risk of Rejection
Thorough Preparation and Research
The most effective way to avoid visa rejection is thorough preparation before applying:
- Research Country-Specific Requirements: Each nation has unique documentation and eligibility standards
- Understand Your Visa Category: Ensure your planned activities align with your visa type
- Check Processing Times: Apply with sufficient lead time before travel
- Review Sample Applications: Many immigration websites provide examples
Honesty and Consistency
Maintaining consistency throughout your application materials and interview is essential:
- Ensure all dates, names, and information match across documents
- Never provide false information, even for seemingly minor details
- Address potential concerns proactively rather than hiding them
- If you’re unsure about something, seek clarification rather than guessing
Providing Strong, Verifiable Evidence
Documentation quality often determines visa outcomes:
- Provide original documents when required
- Include certified translations for non-English documents
- Organize materials logically with a cover letter explaining contents
- For critical evidence (like financial or employment documentation), include multiple forms of proof
Double-Checking All Documents and Forms
Before submission, thoroughly review everything:
- Check forms for completeness (no blank fields unless instructed)
- Verify all required signatures are present
- Ensure photos meet exact specifications
- Confirm payment of correct fees
- Make copies of everything for your records
Consider Professional Assistance
For complex situations or after previous rejections, professional help may be worthwhile:
- Immigration attorneys can provide guidance tailored to your circumstances
- Visa consultants familiar with specific countries can offer practical advice
- University international offices assist students with study visa applications
- Employer HR departments often support work visa applicants
Why Will my Visa be Rejected?
Reasons Your Visa May Be Rejected
Visa applications can be rejected for various reasons depending on the type of visa and the applicant’s circumstances. Below are common reasons for visa rejections:
- Failure to Prove Strong Ties to Home Country
U.S. law assumes every applicant is an intending immigrant until proven otherwise. If you fail to demonstrate strong ties (e.g., family, employment, property) that compel you to return home after your visit, your visa may be denied under INA Section 214(b). - Incomplete or Incorrect Application
Errors or omissions in Form DS-160, such as inaccurate information or missing details, can result in a rejection under INA Section 221(g). - Insufficient Financial Evidence
If you cannot prove that you have sufficient funds to cover your trip expenses or provide unclear financial documentation, your application may be denied. - Failure to Provide a Clear Travel Purpose
Not presenting a clear and detailed travel itinerary or failing to justify the purpose of your visit can lead to rejection. - Previous Immigration Violations
Overstaying a previous visa or violating U.S. immigration laws may result in denial under INA Sections 212(a)(9)(B)(i) or 212(a)(6)(C)(i). - Criminal History
A criminal record involving moral turpitude, drug offenses, or other serious crimes can make you inadmissible under INA Section 212(a). - Lack of Preparation for Visa Interview
Being unprepared for the interview, giving inconsistent answers, or failing to explain why you qualify for the visa category can lead to denial. - Misrepresentation or Fraud
Providing false information or fraudulent documents during the application process results in permanent ineligibility under INA Section 212(a)(6)(C)(i). - Public Charge Concerns
If it is determined that you are likely to become a public charge in the U.S., your visa may be denied under INA Section 212(a)(4). - Applying from High-Risk Countries
Applicants from countries with high visa refusal rates face stricter scrutiny and higher chances of rejection. - Pending Immigrant Petition
Having an active immigrant petition (e.g., I-130) makes it harder to prove nonimmigrant intent when applying for tourist or student visas. - Technical Issues with Supporting Documents
Missing required documents like proof of admission (for students), financial sponsorship letters, or valid passports can result in temporary refusal under INA Section 221(g).
To avoid rejection, ensure all forms are accurate, provide strong evidence of ties to your home country and financial stability, prepare thoroughly for the interview, and comply with all U.S. immigration laws.
Can You Get a US Visa After 3 Rejections?
Yes, you can apply for a US visa after three rejections. There is no limit to the number of times you can apply for a US visa. However, each application must be submitted with updated information or evidence to address the reasons for previous denials.
Key Considerations:
- Understand the Reason for Previous Denials
Each rejection should have been accompanied by an explanation under specific sections of U.S. immigration law (e.g., INA 214(b), 221(g), etc.). Identifying and addressing these reasons is critical before reapplying. - Provide New Evidence or Address Changes in Circumstances
If your visa was denied under INA 214(b) (failure to prove strong ties to your home country), you must present stronger evidence of ties, such as employment, family obligations, or property ownership. - Reapply with Updated Documentation
For refusals under INA 221(g) (missing documents), ensure all required documents are submitted within one year or file a new application if the time has lapsed. - Seek Legal Guidance if Necessary
If the denial involves complex issues like fraud (INA 212(a)(6)(C)) or unlawful presence (INA 212(a)(9)(B)), consulting an immigration attorney may help navigate waivers or other remedies.
Final Note: While there is no restriction on reapplying, repeated applications without addressing prior issues are unlikely to succeed.
Why is my Visa Getting Declined?
Reasons Your Visa May Be Declined
Visa denials can occur for various reasons, depending on the type of visa and your specific circumstances. Below are the most common reasons why your visa might be getting declined:
- Incomplete or Incorrect Application
Errors or omissions in your application form (e.g., Form DS-160) can lead to denial. Double-check all fields for accuracy and completeness. - Insufficient Supporting Documentation
Missing or inadequate documentation, such as proof of financial stability, travel itinerary, or ties to your home country, can result in a refusal. - Failure to Prove Strong Ties to Home Country
If you cannot demonstrate strong ties (e.g., employment, family, property) that ensure your return after visiting the U.S., your application may be denied under INA section 214(b). - Previous Immigration Violations
Overstaying a previous visa or entering the U.S. illegally can make you ineligible for future visas. - Criminal History or Fraud
A criminal record or providing false information/documents during the application process can lead to permanent ineligibility under INA section 212(a)(6)(C)(i). - Financial Instability
Failing to show sufficient funds to cover your trip expenses may result in denial under INA section 212(a)(4) (“public charge”). - Inadequate Interview Performance
Poor preparation for the consular interview, inability to answer questions clearly, or appearing dishonest can negatively impact your application. - Health Concerns
Having a communicable disease or other health issues that pose a public risk may lead to denial. - Applying from a Third Country
Applying outside of your home country often increases scrutiny and raises denial rates. - Suspicion of Immigration Intent
If consular officers suspect you intend to immigrate permanently rather than visit temporarily, they may deny your visa.
You may be interested in: CRS Tool Canada | Your Key to Navigating Immigration
What is the most common reason for visa refusal?
- Understanding Visa Refusal Reasons
Visa refusals can occur for various reasons, including incomplete applications, lack of financial proof, misrepresentation, or past immigration violations. However, one reason consistently stands out as the most common. - Reviewing Sources
Across multiple authoritative sources, the most frequently cited reason for visa refusal is related to the applicant’s inability to demonstrate strong ties to their home country or failure to prove non-immigrant intent. - Legal Basis
Under U.S. immigration law (INA Section 214(b)), all applicants for non-immigrant visas are presumed to be intending immigrants unless they can convince the consular officer otherwise by showing compelling ties to their home country. - Conclusion
Based on this analysis and corroborated by multiple sources, the most common reason for visa refusal is clear.
The most common reason for visa refusal is the applicant’s failure to demonstrate strong ties to their home country or prove non-immigrant intent.
Conclusion: Visa rejection is often a preventable outcome stemming from issues related to documentation, finances, demonstrating genuine intent, or meeting eligibility requirements. By understanding the common reasons why visas get rejected, you can approach your application process with better preparation and greater confidence.
Remember that immigration officers are primarily concerned with ensuring that:
- You have legitimate reasons for travel
- You will comply with visa conditions
- You will return to your home country as required
- You won’t pose security, health, or financial burdens
When your application clearly addresses these concerns with strong supporting evidence, your chances of approval increase significantly.
The visa application process may seem daunting, but approaching it with thorough preparation, honest representation of your circumstances, and attention to detail can make the difference between disappointment and success. Whether you’re planning your first international journey or have faced rejection in the past, understanding these common pitfalls puts you in a stronger position for your next application.
Take the time to prepare properly, seek assistance when needed, and present your case clearly—your travel dreams may be closer to reality than you think.
Have you experienced visa rejection? What challenges did you face in the application process? Share your experiences in the comments below to help other travelers learn from your journey.
Sources:
- U.S Department of State – Visa Denials
- U.S Embassy Morocco – Why Was My Visa Refused?
- Boundless – Common Travel Visa Denials
- Travel.State.Gov – Administrative Processing
- VisaRefusal.com – Reasons for Student Visa Denials
- Travel.State.Gov – Ineligibilities and Waivers
- Immigration and Nationality Act (INA)




